Using AI Agents With Dreamdata via MCP
tl;dr Dreamdata customers already use our Data Warehouse to run custom analytics queries and power external BI tools. Now it’s possible to connect your Data Warehouse to AI assistants to enable powerful agentic workflows.
The background
What is an AI agent?
By “AI agent” we mean an application powered by a Large Language Model (LLM) that can chat, reason, and take actions using external tools. Examples of popular AI agents include Claude, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini.
What is MCP?
MCP stands for **Model Context Protocol.** It is a standardized way for AI agents to connect with external data sources and tools.
How can I use MCP to give my AI Agent access to Dreamdata?
Dreamdata customers with the Data Warehouse add-on can access their data through several platforms, including Google BigQuery, Amazon S3, Snowflake, and Microsoft Azure Storage.
Under the hood, though, our Data Warehouse is implemented on top of Google BigQuery. This lets us take advantage of Google’s new managed MCP server for BigQuery to easily connect AI agents to Dreamdata.
This blog post walks you through enabling the MCP server and connecting to your AI agent. (We’ll use Anthropic’s Claude, but the setup process is similar for any agent that supports MCP tools, including custom agents that run in your own infrastructure).
Prerequisites
Before exposing the Data Warehouse to your AI agent you must enable the BigQuery Data Warehouse in Dreamdata. Follow these setup instructions to enable the Data Warehouse.
After following those instructions, you’ll need the name of your GCP project and the name of the Data Warehouse BigQuery dataset in that project.
Setup
GCP
The first steps in the setup involve enabling the hosted MCP server for BigQuery in Google Cloud Platform. If you completed the prerequisites above, you should have the tools and permissions necessary to complete this step.
1. In the GCP project where your Data Warehouse is hosted, enable the hosted MCP API using the gcloud command line interface (CLI):
gcloud services enable bigquery.googleapis.com --project=${BIGQUERY_PROJECT}
gcloud beta services mcp enable bigquery.googleapis.com --project=${BIGQUERY_PROJECT}
This exposes an MCP server for BigQuery at the following HTTP endpoint: https://bigquery.googleapis.com/mcp which is managed and hosted by Google Cloud.
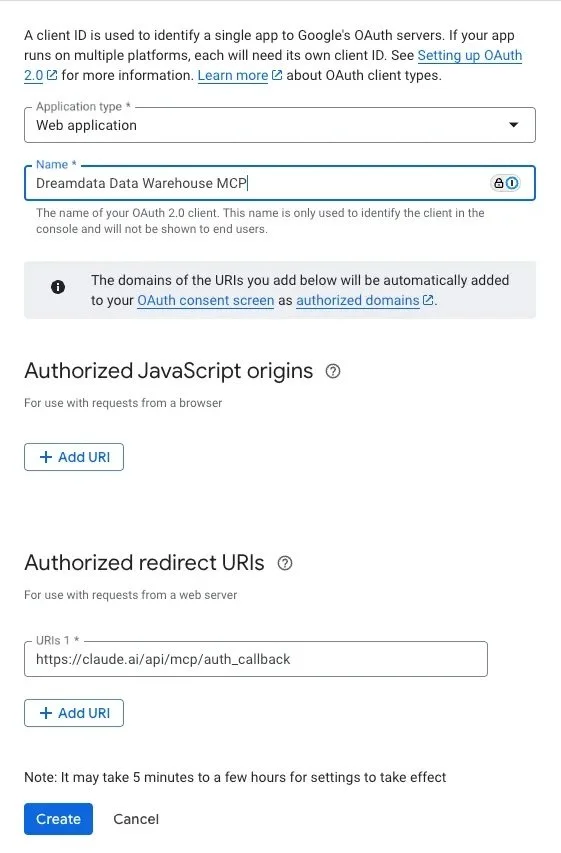
2. Create an OAuth application to allow your users to authenticate with the MCP server. In the Google Cloud console, go to Google Auth Platform > Clients > Create client.
a. Create a “Web Application” and give it a meaningful name. Since we’re using Claude as our agent in this example, we’ll set the Claude remote MCP auth callback URL as the Authorized redirect URI.
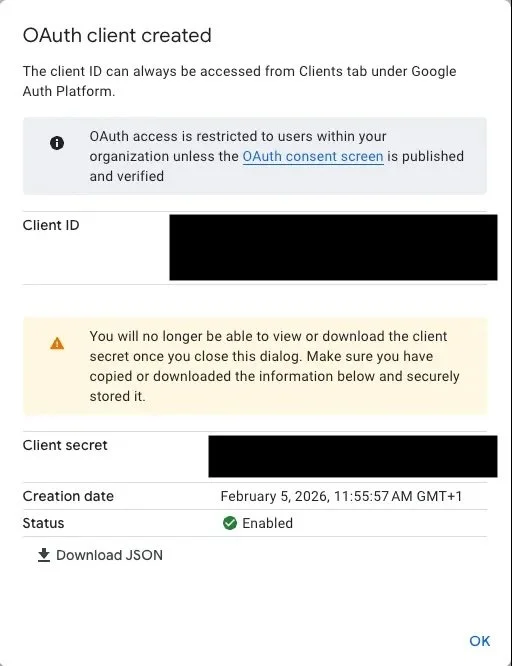
b. Once the Client is created, you’ll be shown the Client ID and Client secret. Store these securely; you’ll need them in order connect the AI agent.
3. Ensure that your users have the appropriate IAM permissions to access the Data Warehouse via MCP. You can grant permissions in the IAM admin page in Google Cloud Console. At a minimum, any users you want to access your Data Warehouse will need the following roles:
AI Agent (e.g. Claude)
The second part of the setup takes place in your AI platform. The exact steps will differ based on the agent you use. In this example, we’ll use Claude to illustrate the general procedure.
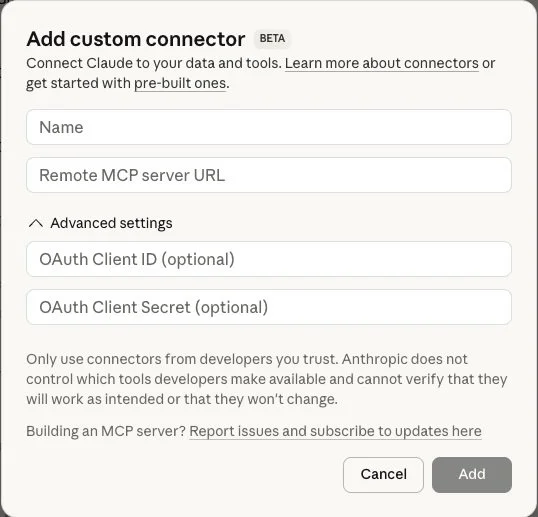
1. As an admin in Claude AI, create a Custom Connector. Use the following values:
a. Remote MCP server URL: https://bigquery.googleapis.com/mcp
b. OAuth Client ID: The Client ID from your GCP OAuth client
c. OAuth Client Secret: The Client Secret from your GCP OAuth secret
2. Once the connector is created, users in your Claude Organization will be able to enable the connector and authenticate as themselves by navigating to Settings > Connectors and clicking “Connect”.
3. From here, Claude users will be asked to authenticate with the connector, after which they will be able to interact with your Dreamdata data via the agent. See Benefits below for some possible use cases.
Benefits
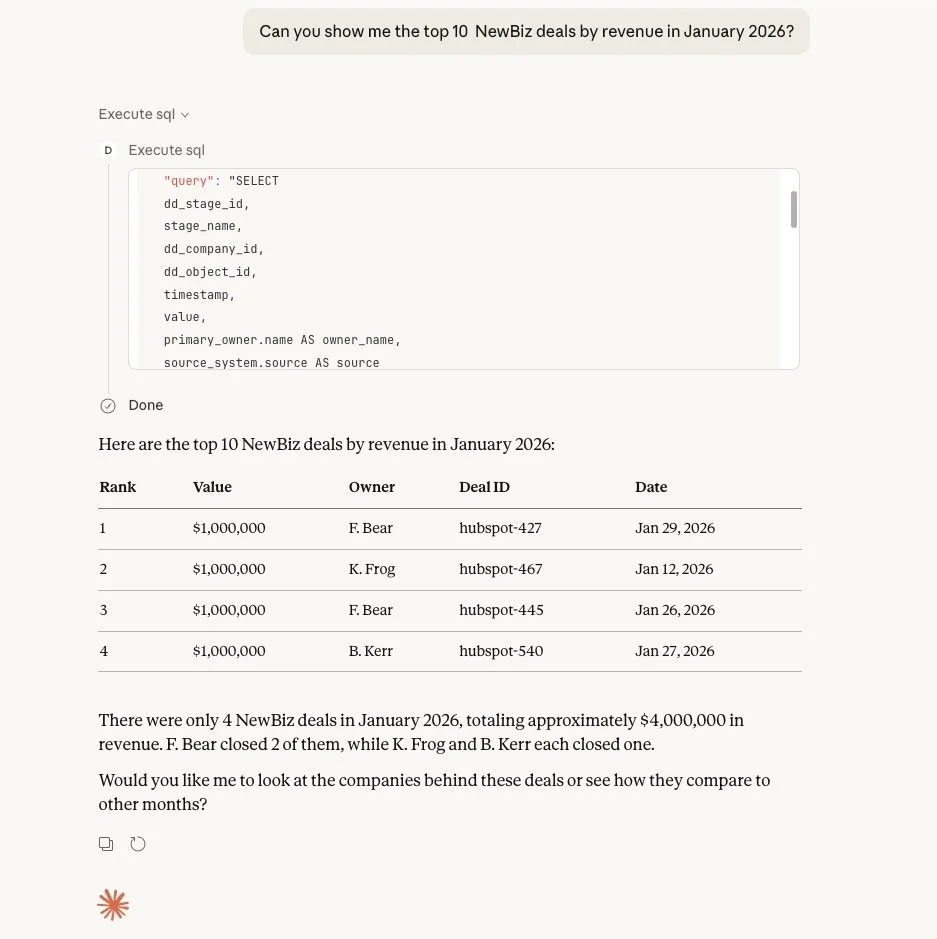
LLM-based agents equipped with tools like these are good at performing exploratory data analysis. For example, you can use them to navigate the Data Warehouse tables:
You can also ask natural language questions of the data and the agent will propose and execute a query to answer your question:
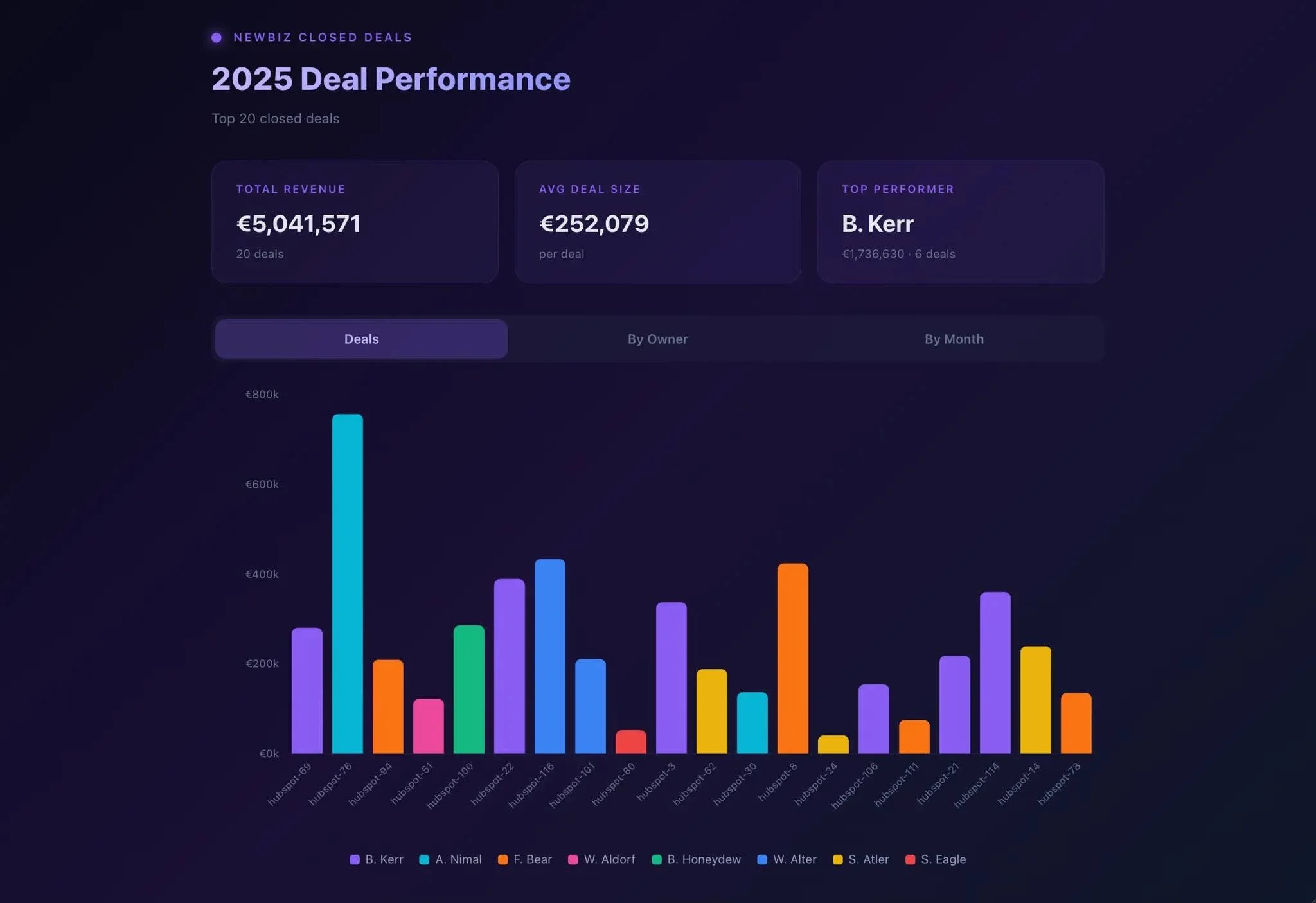
Agents are also great at creating custom visualizations of data like this:
Use cases are not limited to data analysis. Because this the data is exposed through an MCP tool, anything your agent is capable of can use your Data Warehouse data for context. For example, you could build custom agentic workflows (e.g. trigger an action when the data changes).
Considerations
Data privacy and security
In this setup, your agent acts on behalf of your users to query your Data Warehouse data. This means that the agent can access the same data as your users in your Data Warehouse. Make sure you understand how the agent handles data it accesses. It should comply with your organization’s requirements for data privacy, security, residency, etc.
The tools that your agent has access to are limited to the ones that the hosted MCP server exposes for BigQuery. (If you’re interested in other tools, we’d love to hear from you).
This is fundamentally a “text-to-SQL” setup, meaning that the agent must use BigQuery tools to infer the meaning of the data from the schema, structure, and existing data in your Data Warehouse. A more sophisticated setup with a semantic layer would generally lead to better results.
Outputs from foundation models are fundamentally non-deterministic and must be checked for correctness.
Conclusion
It’s easier than ever before to bring your Dreamdata data into your AI agent of choice using an MCP connection to the Data Warehouse.
If you’re already using your own AI agents with Dreamdata to enable agentic workflows, we’d love to hear from you. If you’re interested in learning more about the Data Warehouse or MCP use-cases, please let us know!